According to experts, the XB 1.16 strain may be responsible for the increase in Kovid cases in the nation. According to the Insakag study, nationally there are 349 occurrences of this new variant way.
Just a few days ago, the country has been seeing an influx of Kovid-19 (Coronavirus) cases together with Influenza (Influenza), according to national health data. Is the number of daily Kovid-positive cases affected by the introduction of the new variant?
XBB.1.16:New Covid Varient
There are concerns. In this context, genome sequencing of Kovid-positive patients revealed that 349 instances were connected to the XBB.1.16 variation (Genome Sequencing). Experts predict that this variant will be responsible for Kovid’s latest boom in the country.
In January, two occurrences employing the XBB1.16 variant were reported for the first time in national email. In February, they released 140 models. March saw the identification of an additional 207 by the Indian Sarskov-2 Genomics Collaboration (INSACOG ).
InSakag said that there were 349 XBB.1.16 models in nine states and central regions. In Maharashtra, 105 variant cases came to light, compared to 93 in Telangana, 61 in Karnataka, and 54 in Gujarat.
Dr. Randeep Guleria, former director of Aims, also stated that a new variation might be responsible for Kovid’s recent nationwide expansion. Therefore, there is no cause for concern unless a severe sickness or death occurs. The virus is undergoing changes, although few new variations are emerging.
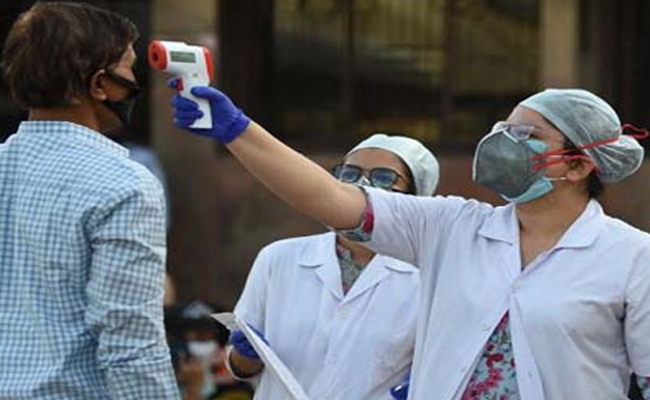
Instances of Regent Kovid are on the rise around the nation. The daily case count has surpassed 1300. Yesterday three folks passed away. After 140 days, there was an increase in the number of cases at this level.
To this purpose, the Prime Minister conducted a comprehensive assessment with the chiefs of the health department. Individuals who are cautious with regards to the Kovid and Influenza viruses will adhere to the Kovid laws. Authorities have been instructed to sequence their genomes intensively, especially for the early identification of novel variations.

